The production of summer corn is in a hot and rainy season. The supply of soil nutrients is strengthened this season. Experts suggest that farmers should estimate and make full use of local water and heat resources, rationally distribute fertilizer according to the seasonal characteristics of winter wheat-summer corn rotation system, and improve fertilizer. Utilization rate, achieving high productivity and high efficiency, reducing environmental pollution.
Now it has entered the summer harvest summer season, and most of the North China region is the winter wheat-summer corn rotation system. In the management of production, especially the nutrient management of fertilization, it is necessary to integrate the two crops of winter wheat and summer maize as a whole. It is necessary to see that the production of summer maize is in a hot and rainy season, and the supply of soil nutrients is strengthened this season. And make full use of the local water and heat resources, according to the seasonal characteristics of the winter wheat-summer corn rotation system, rationally distribute fertilizer, improve utilization rate, achieve high yield and high efficiency, and reduce environmental pollution.
In terms of production arrangements, we must also see that the planting of summer corn is in a particularly tight season. In many areas, it is speeding up the harvest, and it is too late to roll over and deep-base fertilizer. Some areas are posted after wheat harvest. Sowing, so summer corn usually does not apply base fertilizer, only apply fertilizer and top dressing. Therefore, it is necessary to explain the fertilization characteristics of summer corn here for reference by farmers.
From the winter wheat-summer corn rotation system, summer maize has a short growth period of about 100 days, which is generally about 20 days shorter than spring corn. The total amount of fertilizer absorbed during the whole growth period was less than that of winter wheat, but the time of absorption was relatively concentrated and advanced. It has characteristics in terms of the amount of nutrient demand and the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Generally, 100 kg of summer corn kernels need to absorb nitrogen (N) 2.5 to 2.7 kg, phosphorus (P2O5) 1.1 to 1.4 kg, and potassium (K2O) 3.2 to 3.8 kg. The ratio of absorption of NPK (N: P2O5: K2O) is 1:0.50:1.35 on average. The recommended fertilization amount for general production level in production is 12 kg/mu for nitrogen fertilizer (N), 3 to 4 kg/mu for phosphorus (P2O5), and 4 to 6 kg/mu for potassium (K2O). In the fertilization period, the absorption time of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients in summer maize is earlier than that in spring maize, and the absorption peak is reached at the jointing and booting stage. According to this feature, fertilization should be applied before the peak of fertilizer demand.
Firstly, compared with nitrogen absorption, the nitrogen uptake of spring maize seedlings only accounted for 2.1% of the total nitrogen uptake during the whole growth period, 51.2% from the jointing to the heading stage, and 46.7% in the later stage. The summer maize was characterized by sucking at the seedling stage. Nitrogen is more than 9.7% of the total nitrogen uptake during the whole growth period, accounting for 78.5% in the medium term and only 11.9% in the later period. The amount of potassium absorbed by summer maize is large in the seedling stage, and then gradually decreases. The cumulative potassium absorption is the fastest in the late stage of jointing, and reaches the peak in the flowering stage, and the absorbed nutrients are significantly reduced. In view of the stage characteristics of summer corn absorption and nutrient process, the fertilization program of summer corn generally consists of seed fertilizer and top dressing. In order to ensure the harvest of summer corn, the principle of “early†and “heavy†should be mastered in topdressing, and it is expected to achieve high yield and high efficiency.
In the rotation, the response of summer maize to phosphate fertilizer is not as great as that of winter wheat. For this reason, the application principle of phosphate fertilizer is to re-apply phosphate fertilizer on winter wheat (about 2/3 of the annual phosphorus application), and the relatively light application of phosphate fertilizer in summer maize (roughly in the anniversary). 1/3 of the amount of phosphorus applied, although there is no need to apply more phosphorus fertilizer, but the precise amount of phosphate fertilizer should highlight an "early application", generally applied in the seedling stage. The suitable dosage range is 2-5 kg/mu of phosphorus. After the Miaoqi was applied to the soil, it would be late if the phosphate fertilizer was applied during the period of the big bell. The late application of the phosphate fertilizer also had an effect on the yield.
Summer corn and winter wheat rotation, wheat is directly sown after harvesting, sometimes applying some fertilizer when planting, and topdressing adopts the principle of “before and then lightâ€. The contribution of early application of phosphate fertilizer to summer maize yield is to increase the number of grains, which is shown to reduce the baldness. The key period for phosphorus application in summer maize is from the end of June, and no later than the first month of July.
In the topdressing operation, in the past, 2/3 of the total amount of nitrogen was applied during the jointing stage, and the remaining 1/3 was applied to the large bell mouth. Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers were generally applied at the seedling stage. Recent studies have shown that due to the live broadcast of summer corn, the basic fertilizer is not applied, and the seed fertilizer is also insufficient. Therefore, the topdressing should be applied early, and the nitrogen application rate in the high-yield field should account for 30% of the total nitrogen application rate. Increase the proportion by 40%. The general trend is to topdress the first time after the corn seedlings, all the phosphorus and 1/2 of the potassium, 1/3 of the nitrogen for topdressing, trenching or digging to apply a depth of 10 cm. In the jointing stage or the big bell period, the remaining 2/3 nitrogen fertilizer and 1/2 potash fertilizer are applied as top dressings.
In the hot and rainy season, in order to prevent the loss of ammonium nitrogen fertilizer and improve the fertilizer utilization rate, the topdressing of summer corn should be ditched or burrowed and fertilized, and covered with soil, do not apply the surface.
Author: Cao Yiping
Source: Shaanxi Science and Technology News
According to its material, performance can be divided into: ordinary carbon structural steel, low alloy steel, alloy steel.
According to their different purposes can be divided into: cold forming steel, structural steel, automotive structural steel, corrosion resistant structural steel, mechanical structural steel, welded cylinders and pressure vessel steel, pipeline steel, etc.
Now it has entered the summer harvest summer season, and most of the North China region is the winter wheat-summer corn rotation system. In the management of production, especially the nutrient management of fertilization, it is necessary to integrate the two crops of winter wheat and summer maize as a whole. It is necessary to see that the production of summer maize is in a hot and rainy season, and the supply of soil nutrients is strengthened this season. And make full use of the local water and heat resources, according to the seasonal characteristics of the winter wheat-summer corn rotation system, rationally distribute fertilizer, improve utilization rate, achieve high yield and high efficiency, and reduce environmental pollution.
In terms of production arrangements, we must also see that the planting of summer corn is in a particularly tight season. In many areas, it is speeding up the harvest, and it is too late to roll over and deep-base fertilizer. Some areas are posted after wheat harvest. Sowing, so summer corn usually does not apply base fertilizer, only apply fertilizer and top dressing. Therefore, it is necessary to explain the fertilization characteristics of summer corn here for reference by farmers.
From the winter wheat-summer corn rotation system, summer maize has a short growth period of about 100 days, which is generally about 20 days shorter than spring corn. The total amount of fertilizer absorbed during the whole growth period was less than that of winter wheat, but the time of absorption was relatively concentrated and advanced. It has characteristics in terms of the amount of nutrient demand and the ratio of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium. Generally, 100 kg of summer corn kernels need to absorb nitrogen (N) 2.5 to 2.7 kg, phosphorus (P2O5) 1.1 to 1.4 kg, and potassium (K2O) 3.2 to 3.8 kg. The ratio of absorption of NPK (N: P2O5: K2O) is 1:0.50:1.35 on average. The recommended fertilization amount for general production level in production is 12 kg/mu for nitrogen fertilizer (N), 3 to 4 kg/mu for phosphorus (P2O5), and 4 to 6 kg/mu for potassium (K2O). In the fertilization period, the absorption time of nitrogen, phosphorus and potassium nutrients in summer maize is earlier than that in spring maize, and the absorption peak is reached at the jointing and booting stage. According to this feature, fertilization should be applied before the peak of fertilizer demand.
Firstly, compared with nitrogen absorption, the nitrogen uptake of spring maize seedlings only accounted for 2.1% of the total nitrogen uptake during the whole growth period, 51.2% from the jointing to the heading stage, and 46.7% in the later stage. The summer maize was characterized by sucking at the seedling stage. Nitrogen is more than 9.7% of the total nitrogen uptake during the whole growth period, accounting for 78.5% in the medium term and only 11.9% in the later period. The amount of potassium absorbed by summer maize is large in the seedling stage, and then gradually decreases. The cumulative potassium absorption is the fastest in the late stage of jointing, and reaches the peak in the flowering stage, and the absorbed nutrients are significantly reduced. In view of the stage characteristics of summer corn absorption and nutrient process, the fertilization program of summer corn generally consists of seed fertilizer and top dressing. In order to ensure the harvest of summer corn, the principle of “early†and “heavy†should be mastered in topdressing, and it is expected to achieve high yield and high efficiency.
In the rotation, the response of summer maize to phosphate fertilizer is not as great as that of winter wheat. For this reason, the application principle of phosphate fertilizer is to re-apply phosphate fertilizer on winter wheat (about 2/3 of the annual phosphorus application), and the relatively light application of phosphate fertilizer in summer maize (roughly in the anniversary). 1/3 of the amount of phosphorus applied, although there is no need to apply more phosphorus fertilizer, but the precise amount of phosphate fertilizer should highlight an "early application", generally applied in the seedling stage. The suitable dosage range is 2-5 kg/mu of phosphorus. After the Miaoqi was applied to the soil, it would be late if the phosphate fertilizer was applied during the period of the big bell. The late application of the phosphate fertilizer also had an effect on the yield.
Summer corn and winter wheat rotation, wheat is directly sown after harvesting, sometimes applying some fertilizer when planting, and topdressing adopts the principle of “before and then lightâ€. The contribution of early application of phosphate fertilizer to summer maize yield is to increase the number of grains, which is shown to reduce the baldness. The key period for phosphorus application in summer maize is from the end of June, and no later than the first month of July.
In the topdressing operation, in the past, 2/3 of the total amount of nitrogen was applied during the jointing stage, and the remaining 1/3 was applied to the large bell mouth. Phosphorus and potassium fertilizers were generally applied at the seedling stage. Recent studies have shown that due to the live broadcast of summer corn, the basic fertilizer is not applied, and the seed fertilizer is also insufficient. Therefore, the topdressing should be applied early, and the nitrogen application rate in the high-yield field should account for 30% of the total nitrogen application rate. Increase the proportion by 40%. The general trend is to topdress the first time after the corn seedlings, all the phosphorus and 1/2 of the potassium, 1/3 of the nitrogen for topdressing, trenching or digging to apply a depth of 10 cm. In the jointing stage or the big bell period, the remaining 2/3 nitrogen fertilizer and 1/2 potash fertilizer are applied as top dressings.
In the hot and rainy season, in order to prevent the loss of ammonium nitrogen fertilizer and improve the fertilizer utilization rate, the topdressing of summer corn should be ditched or burrowed and fertilized, and covered with soil, do not apply the surface.
Author: Cao Yiping
Source: Shaanxi Science and Technology News
ã€Comment】 ã€Print this article】 ã€Close this page】 ã€Large, medium and small】
The main raw material of hot rolled strip coil is Continuous casting slab, it will be made into steel coil by roughing mill group and finishing mill group after Heating.
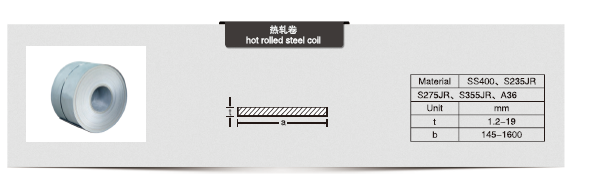
According to its material, performance can be divided into: ordinary carbon structural steel, low alloy steel, alloy steel.
According to their different purposes can be divided into: cold forming steel, structural steel, automotive structural steel, corrosion resistant structural steel, mechanical structural steel, welded cylinders and pressure vessel steel, pipeline steel, etc.
Hot Rolled Steel Coil, Cold Rolled Steel Coil,Hot Rolled Coil,Hot Rolled Steel Coil,Hot Rolled Strip Coil,Steel Coil
TIANJIN ZHENXIANG STRIP PROCESSING CO., LTD. , http://www.zhenxiangsteel.com