Inspired by the natural water cycle, the use of sunlight to drive water evaporation to obtain clean fresh water has attracted widespread attention from researchers. Under natural evaporation conditions, the use of sunlight is low and the actual evaporation is slow. Researchers have tried to apply photothermal film materials with good light absorption and photothermal conversion capabilities to sunlight-driven evaporation systems to increase evaporation efficiency. Previous studies have shown that a rough surface with a controllable microstructure can effectively reduce the diffuse reflectance of light and achieve effective absorption of all wavelengths of sunlight, which is conducive to efficient water evaporation. However, the construction method of the surface microstructure is relatively complicated, and often requires special equipment or means to assist in the completion, thereby increasing the difficulty and cost of preparing the membrane material.
According to this, the Membrane Separation and Catalysis Team led by Jiang Heqing, a researcher at the Institute of Bioenergy and Bioprocess Technology of the Chinese Academy of Sciences in Qingdao, proposed using the compounding strategy of nanomaterials in different dimensions to realize the regulation of the surface microstructure of the photothermal film, thereby improving the light capturing efficiency. Get ideal photo-thermal evaporation efficiency. The researchers combined the two-dimensional graphene with one-dimensional carbon nanotubes to achieve perturbation of the ordered structure of the single component and increased the surface roughness of the photothermal film. Through the optimization of this surface microstructure, the diffuse reflection in the solar spectrum can be reduced to 4.7% or less, and the surface temperature of the film under illumination can reach 77°C. Disordered packing increases the porosity within the membrane and facilitates the transport and diffusion of water molecules within the membrane. Compared with natural evaporation, the efficiency of the evaporation process based on this kind of nanocomposite photothermal film is increased by 190%, and the utilization rate of sunlight is more than 80%. In practical applications, the nanocomposite photothermographic film proposed in this study can not only maintain stable performance in simulated water samples containing acid, alkali, and organic pollutants, but also can accelerate water evaporation in seawater of different salt content and exhibit Excellent fresh water production capacity. The preparation process of such a photothermal composite film is simple and can be constructed on different porous substrates. The results of this study are expected to promote the application of solar-driven clean freshwater production and achieve efficient, green, sustainable seawater desalination and freshwater protection under emergency conditions.
Related research results were published in the Journal of Materials Chemistry A. The study was funded by the National Natural Science Foundation of China, the Natural Science Foundation of Shandong Province, and the Qingdao Minsheng Science and Technology Project.
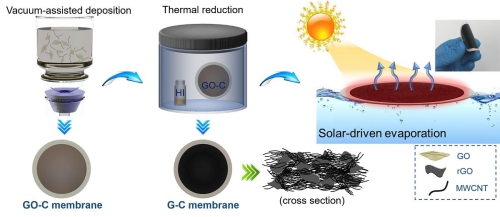
Figure 1. Preparation of nanocomposite photothermographic film based on two-dimensional graphene and one-dimensional carbon nanotubes
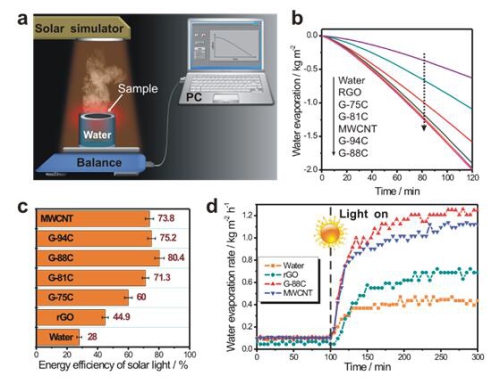
Figure 2. On-line Photothermal Evaporation Test System (a) and Photothermal Film Material Solar Drive Evaporation Performance Test (bd)
Machine Room Elevator,Elevator Machine,Lift With Machine Room,Roomless Elevator
Homefriend&FUJI Elevator Co.,Ltd , https://www.jfujilift.com