The residual pressure of the spring of the process shot peening is uniform, and the residual compressive stress value is similar to the residual compressive stress of the inlet spring. After shot peening, the residual compressive stress field and the plastic deformation structure are formed on the surface and surface layer of the spring material. Therefore, shot peening has two strengthening factors, tissue strengthening and stress strengthening. The surface strain layer consists of fine subgrains and high-density dislocations, which change the morphology and various characteristics of the slip zone, hinder the fatigue cracks from sprouting on the surface and subsurface of the material, thus prolonging the initiation of fatigue cracks. . When there is residual compressive stress, the fatigue source moves to the subsurface, and the crack initiation position gradually moves to the surface as the applied alternating stress increases. In the case of surface cracks, the residual compressive stress can reduce the tensile stress peak caused by the external force at the crack tip, or cause the crack to be closed during the fatigue process, and as a result, the threshold value of the surface crack propagation is improved. The hot pressing process test uses AH.1 type high frequency fatigue testing machine, frequency 3Hz, DHG102 type electric drying oven, and self-made hot pressing fixture for hot pressing process test. The hot press test temperature was 150 ° C and the spring was compressed to about 30. According to the spring stress and load loss rate requirements, three kinds of hot pressing process PH (specific for intake valve spring), PB, PL are designed. The springs treated by the three processes are subjected to a comparative test. The evaluation index is the percentage of the decrease of the P: value, and the fatigue life of the spring is also evaluated. The standard requires the fatigue life to be 2.3x1 and does not break after the protection cycle. The stress amplitude of the fatigue test is 720.5 soil 165.SMpa, and the test time is 200h. Through the test, the samples of each process did not break after the fatigue test, and the fatigue life reached the standard requirement. After the test, the load loss rates of the PB and PL hot pressing processes were 6.8% and 3.6%, respectively, that is, the P: values ​​decreased by slN and 27N, respectively, while the pH process load loss rate was negative. In order to further test the load loss rate of each process, a hot press relaxation test was carried out in accordance with the standard QZZI 118-1994. The shot peening process shot peening is performed on a mechanical centrifugal shot peening machine. Using the diameter of the pellets of 0.9, the different shot peening times and times were selected to apply the A, B and C shot peening techniques to the valve springs made of the domestic 67CrVA springs.
Using the diameter of the pellets of 0.9, the different shot peening times and times were used to apply the A, B and C shot peening techniques to the valve springs made of the domestic 67CrVA spring steel wires. Two kinds of high-frequency fatigue relaxation were the same as the above-mentioned high-frequency test. The test was carried out on a self-made test machine with a rotation speed of 1300 r/min, an assembly height of 46 rim, a stroke of 13.3 rnrn, and a test time of 400 h. The hot-press relaxation curve should have two stages. The first stage is generally formed within 30 minutes, that is, the load loss rate has reached about 13% within 30 minutes without hot pressing, and about 4% after hot pressing, due to the short time. The first stage curve cannot be drawn. As the relaxation time increases, the load loss rate increases continuously, and the load loss rate does not change after 75 hours. The load loss rate at 75 h is slightly lower than the load loss rate at 16 h in the standard. The MEF3 optical metallographic microscope and Hso-type transmission electron microscope were used to detect the tissue changes before and after the spring relaxation. Before the hot pressing, the structure of the 67CrVA steel wire is tempered martensite, which has the characteristics of lath-like strips, and there are uneven dislocations in the martensite, and the carbides precipitated during tempering are deposited along a positioning direction. The tissues were heat treated at 150 ° C, 840 N for 30 min and 600 h, respectively. After heat and pressure, the black and white, roughly parallel strip-like cell structure appears in some weak regions, and white ferrite and black dislocations accumulate along the movable surface. This structure effectively hinders dislocation motion and strengthens the weaker parts of the tissue that are susceptible to plastic deformation. With the prolonging of the hot pressing time, the dislocations in the structure are seriously deposited between the lath martensite, and the worm-like carbides are deposited in the matrix of the tempered structure, the pinning dislocations, and the dislocation distribution is uneven. Therefore, the anti-relaxation performance of the spring is getting stronger and stronger, the load loss rate is getting smaller and smaller, and the influence of hot pressing on the structure is getting smaller and smaller.
Drywall Screws are a heat-treated process suitable for power tool installation and are mainly used for joining and fastening between wood panels and between wood panels and thin steel sheets.
Wall nail is a class of nails, its name is directly translated from the English Drywall Screw, the most important feature in the appearance of the flared head shape, divided into a double line of fine teeth drywall screws and single line of coarse teeth drywall screws, the biggest difference between the two is that the former thread is double thread.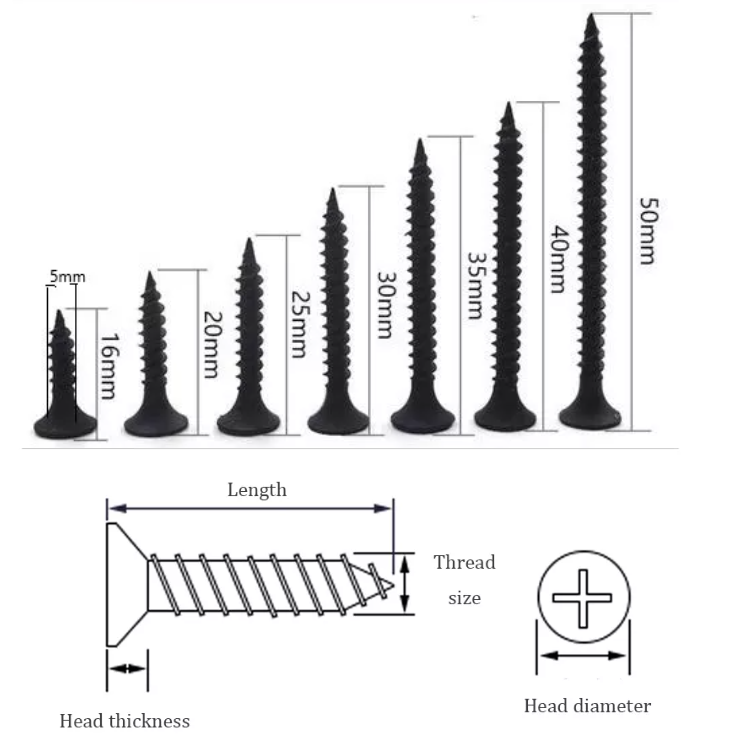
Sheetrock Screws,Collated Screws,Drywall Screw Bit,Screwing Into Drywall
Kunshan Zhonggu Precision Hardware Co., Ltd. , https://www.zgfastener.com