Preparation and Decolorization Performance of Cationic Starch Flocculant MA Bingjie LI Yanping YAN Dongmao TANG Hongbo
(School of Science, Shenyang University of Technology, Shenyang 110178, China)
Abstract: A quaternary ammonium cationic starch flocculant (DS=0.099) was prepared by dry process using potato starch as raw material and 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride as etherifying agent. -8G dye solution was used to simulate printing and dyeing wastewater. The effects of dye concentration, flocculant dosage, decolorization time and wastewater pH on decolorization rate and adsorption amount were studied. The results show that the cationic starch flocculant has good decolorization ability for alkaline printing and dyeing wastewater. The decolorization rate is up to 12.5, the dye concentration is 113.5 mg/L, the flocculant dosage is 120 mg/L, and the decolorization time is 2 h. 63.2%, the adsorption amount is 0.612 mg / mg; the adsorption of acid dye molecules by flocculant is in accordance with Langmuir monolayer adsorption theory.
Key words: cationic starch flocculant decolorization performance CLC number: TS235.1 Document code: A Article ID:1003-0174(2009)07-0113-04 Cationic starch is an important polymer flocculant with excellent Degradability, flocculation and stability of use. Since the 1970s, the use of cationic starch in industrial wastewater treatment in the United States, Japan, Britain, France and other countries has solved the problem of safe, non-toxic and non-secondary pollution of flocculants [1-2]. The produced cationic starch is mainly used in the papermaking and chemical industries, and its application in water treatment has not yet formed an industrial scale [3].
Printing and dyeing wastewater is one of the most harmful and difficult to treat industrial wastewater in China. It is characterized by large amount of wastewater, complex water quality, deep color and difficult biodegradation. Among them, acid dye wastewater is the most serious. Acid dye molecules are relatively small and contain more than one water-soluble group (usually a sulfonic acid group). The dye molecules are ionized in water and have a negative charge [4], because their molecules are small and soluble in water, even at very low levels. Concentration can also cause serious pollution to water bodies, making it difficult to treat wastewater. The quaternary ammonium cationic starch is a natural polymer derivative. The quaternary ammonium group in the molecule has a positive charge, which can interact with the negative charge of the dye molecule, and the adsorption and network bridging of the polymer can make the dye molecule adsorb. On the surface of the polymer, flocculation is deposited on the bridge. In this paper, the quaternary ammonium cationic starch flocculant was prepared by dry process. The decolorization performance and decolorization conditions of cationic dye flocculant on acid dye simulated wastewater were studied. The theory and experiment for the development and application of cationic starch flocculant in dyeing wastewater treatment were studied. in accordance with.
1. Materials and methods 1.1 Raw materials and reagents Potato starch: Heilongjiang Yinhe Starch Group; 3-Chloro-2-hydroxypropylmethylammonium chloride: Dongying Sanjin Chemical Co., Ltd.; Zinc grain: Changzhou Qingfu Metal Products Co., Ltd. Company; Selenium powder: Shanghai Yuhua Chemical Co., Ltd.
1.2 Instruments and equipment Rotary viscometer: DDJ-1 type, Beijing Deli Analytical Instrument Co., Ltd.; Spectrophotometer: WFJ7200 type, Shanghai Unico Electric Co., Ltd.
1.3 Test method 1.3.1 Preparation of cationic starch flocculant Weigh 10 g (dry basis) of potato starch, spray 4% NaOH solution to activate the starch under stirring, mix for 0.5 h, and add the amount of etherifying agent to the amount of NaOH. After rapidly stirring and mixing for 10 min in an ice bath, it was sprayed onto the starch activated by NaOH, stirred for 0.5 h, then transferred to a closed reactor, and the mixture was reacted at a specified temperature and time to obtain a crude product of white solid, which was coarse. The product is immersed in an 80% aqueous solution of ethanol and neutralized to a pH of 6-8 with a small amount of glacial acetic acid, and then washed, filtered, dried, pulverized, and sieved to obtain a quaternary ammonium type cationic starch flocculating agent (hereinafter referred to as a flocculating agent).
.3.2 Preparation of simulated printing and dyeing wastewater Accurately weigh 113.5 mg of fluorescent yellow E-8G dye, put it into a 100mL beaker, add a certain amount of water to dissolve, and then dilute to 1 000 mL to obtain simulated printing and dyeing wastewater. The simulated printing and dyeing wastewater had an absorbance of 2.088, a pH of 7, and a test wavelength of 440 nm.
1.3.3 Decolorization test Accurately weigh a certain amount of flocculant in a 200 mL beaker, add 100 mL of dye wastewater, stir with a stirrer at a speed of 150 r/min for a certain period of time, and let stand for half an hour. The absorbance of the supernatant was measured with a spectrophotometer, and distilled water was used as a reference solution. Use the standard curve to find the corresponding dye concentration C (if the solution absorbance exceeds the standard curve range, the solution is diluted several times and then the absorbance is measured, the solution concentration is the product of the dilution factor and the concentration corresponding to the absorbance) [5]. The flocculation effect was measured by the decolorization rate and the adsorption amount. The formula for calculating the decolorization rate (D) and the adsorption amount (X) is: 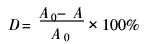
Where: A0 is the absorbance before decolorization of the dye wastewater; A is the absorbance after decolorization of the dye wastewater. 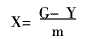
Where: G is the dye mass/mg before decolorization; Y is the dye mass/mg in the wastewater at the time of adsorption equilibrium; m is the flocculant mass/mg added to the dye wastewater.
2 Results and discussion 2.1 Dye solution concentration-absorbance standard curve The absorbance at different wavelengths was measured with a 54 mg/L dye solution, and the maximum absorbance at 440 nm, so the working wavelength of the spectrophotometer was determined to be 440 nm.
Accurately weigh a certain amount of fluorescent yellow E-8G dye, prepare dye solutions at concentrations of 18, 24, 30, 36, 42, 48, 54 mg / L, determine the absorbance of the solution, and draw the dye solution concentration - absorbance standard curve, As shown in Figure 1. 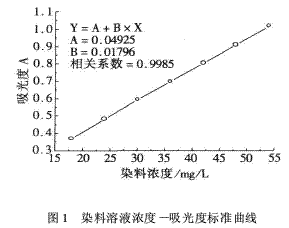
2.2 The effect of decolorization time on decolorization rate and adsorption amount is 113.5 mg/L for dye concentration, 7.0 pH for wastewater, 120 mg/L for flocculant, and 0.5, 1.0, 1.5, 2.0, 3.0 h for decolorization time. The effect of decolorization time on the decolorization rate and adsorption amount is shown in Fig. 2. 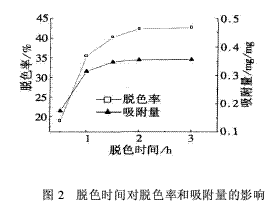
It can be seen from Fig. 2 that when the decolorization time is 0.5 to 1.5 h, the decolorization rate of the flocculant to the wastewater and the adsorption amount to the dye molecules are significantly increased. After 2.0 h of decolorization time, there was no significant change in decolorization rate and adsorption amount. Because the adsorption process of the dye molecules by the flocculant is divided into two stages: the first stage is the diffusion of the dye molecules in the solution to the surface of the flocculant, the process is slow, and the second stage is the positive charge of the flocculant and the negative of the dye molecules. The process of charge interaction and combination is faster. When the adsorption of the dye molecules by the flocculant reaches saturation, that is, the adsorption equilibrium, the decolorization rate and the adsorption amount no longer increase with the extension of the decolorization time. Therefore, a suitable decolorization time is 1.5 to 2.0 h.
2.3 The effect of flocculant dosage on decolorization rate and adsorption amount is 113.5 mg/L dye concentration, 7.0 pH value of wastewater, 2 h decolorization time, and the dosage of flocculant is 50, 200, 500, 1 000, 2 000 mg/L. The effect of flocculant dosage on decolorization rate and adsorption amount is shown in Fig. 3. 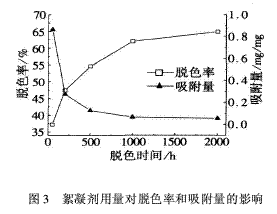
It can be seen from Fig. 3 that as the amount of flocculant increases, the decolorization rate increases, and the adsorption amount gradually decreases. When the flocculant dosage is less than 1 000 mg/L, the decolorization rate and the adsorption amount change significantly, and the flocculant dosage is greater than 1 000 mg. After /L, the change in decolorization rate and adsorption amount tends to be gentle. Because the amount of flocculant is increased, the adsorption surface area is increased, and the amount of adsorption to the dye molecules is increased, and therefore, the decolorization rate is increased. However, when the amount of flocculant is increased to a certain extent, not only the electrostatic interaction between the flocculant molecules and the dye molecules but also the electrostatic repulsion between the flocculant molecules is intensified, which is not conducive to adsorption. factor. Therefore, the change in the decolorization rate and the adsorption amount tends to be gentle. Considering the cost and effect of wastewater treatment, the amount of flocculant can be selected in the range of 500~1 000 mg/L.
2.4 The effect of wastewater pH on the decolorization rate and adsorption capacity is 113.5 mg/L for dye concentration, 2 h for decolorization time, 120 mg/L for flocculant (the same below), and the pH of wastewater is 2.0, 4.1, 6.0, 8.0, 10.0, respectively. 12.5 Under the test conditions, the effect of wastewater pH on the decolorization rate and adsorption capacity is shown in Figure 4. 
It can be seen from Fig. 4 that when the pH of the wastewater is 2-8, the decolorization rate and the adsorption amount decrease slowly with the increase of pH. When the pH is 8.0, the decolorization rate and the adsorption amount increase significantly with the increase of pH. When the pH is 12.5, the decolorization is performed. The rate and the amount of adsorption reached 63.2% and 0.612 mg/mg, respectively, and a larger value was obtained.
2.5 Effect of dye concentration on decolorization rate and adsorption amount When the dye concentrations are 18, 32, 42, 54, 80, 113.5, 150, 200 mg/L, the effect of dye concentration on decolorization rate and adsorption amount is shown in Fig. 5. Show. 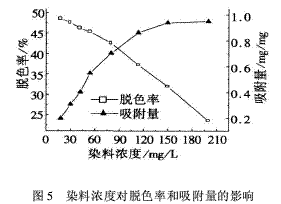
It can be seen from Fig. 5 that as the dye concentration increases, the decolorization rate decreases gradually, while the adsorption amount increases significantly at the dye concentration of 18 mg/L to 113.5 mg/L. After the dye concentration is greater than 150 mg/L, the dye concentration increases. The amount of adsorption does not change much. The adsorption curve obtained by the experiment is basically consistent with the shape of the Langmuir isotherm adsorption line, indicating that the adsorption of the acid dye molecules by the cationic starch flocculant conforms to the Langmuir monolayer adsorption theory [6-9]. The adsorption equation is: 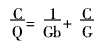
Where: C is the dye concentration/mg/L at the equilibrium of adsorption; Q is the adsorption amount of flocculant at the equilibrium of adsorption/mg/mg; G is the saturated adsorption amount/mg/mg; b is the adsorption constant.
According to the isothermal adsorption equation, C/Q and C are in a linear relationship with a slope of 1/G and an intercept of 1/Gb. Figure 6 is plotted as C/Q versus C. The regression equation is Y = 38.155 82 + 0.606 03 X, and G = 1.65 mg/mg is obtained from the regression equation, and b = 0.015 884. 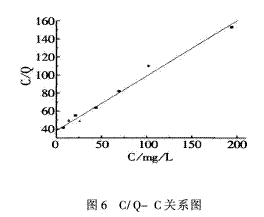
3. Conclusion The quaternary ammonium type cationic starch flocculant was prepared by dry process using potato starch as raw material and 3-chloro-2-hydroxypropyltrimethylammonium chloride as etherifying agent. The degree of product substitution was 0.099. The decolorization test results of the simulated printing and dyeing wastewater show that the cationic starch flocculant has good decolorization ability in alkaline solution; the pH of the wastewater is 12.5, the dye concentration is 113.5mg/L, and the dosage of flocculant is 120 mg/L. Under the condition of 2 h, the decolorization rate was 63.2%, and the adsorption amount was 0.612 mg/mg. In the neutral solution, when the decolorization rate was 54.6~62.0%, the cationic starch flocculant dosage was 500~1 000 mg/L; The adsorption of acid dye molecules by starch flocculant conforms to the Langmuir monolayer adsorption theory. The saturated adsorption capacity is G=1.65 mg/mg and the adsorption constant b=0.015 884. The preparation process of cationic starch flocculant is simple, the flocculation performance is excellent, and it is non-toxic. It is biodegradable and is an environmentally friendly water treatment agent.
references
[1] Zhuang Yafeng, Yao Guosheng, Li Jieli. Decolorization of printing and dyeing wastewater by magnesium hydroxide-starch composite flocculant[J].Chemistry & Bioengineering,2007,24(2):29-31
[2]DENG Yu,LI Lan-qing.Preliminary Study on Dry Synthesis of Cationic Starch Flocculant[J].Journal of Chemical Industry & Industrial Technology,2005,26(1):9-12
[3]Chen Chunxin, Chen Wei, Yuan Yihua, et al. Application of Modified Starch in Printing and Dyeing Wastewater Treatment[J].Food Science,2007,28(10):245-247
[4] Wan Guoping, Wang Jiahe. The basis of dye chemistry [M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2000
[5]有本æ¤. Preparation and application of high-substituted cationic starch [D]. Dalian: Department of Fine Chemical Engineering, Dalian University of Technology, 2000 [6] Wang Zhenglie, Zhou Yaping. Physical Chemistry [M]. Beijing: Higher Education Press , 2000
[7]HamrstrandG E, HofreiterB T, MehltreterC L. Deter mination of the
Txtt of the extent of reaction between epichloro hgdrin andstarch
[J]. Cereal Chem, 1960, 3(7): 5-19
[8]Xu Shimei.Synthesis and application of amphoteric starch[D].Dalian: Department of Applied Chemistry, Dalian University of Technology, 2002
[9] Ketola H Y, Hagberg P F. Modified starch [P]. US, 6670470.2003-12-3.
Spring Steel Stamping Parts,Stamping Welding Parts,Steel Welded Tube,Metal Casting Chair
JIANGSU TONGDE INTERNATIONAL TRADE CO.LTD. , https://www.tongdetrades.com